충분히 쌓여가는
생성자 super() 본문
생성자 super()
조상의 생성자를 호출할 때 사용
조상의 멤버는 조상의 생성자를 호출해서 초기화
참조변수 super와 관계없다
(상속에서 생성자와 초기화 블록은 상속이 불가능하다)
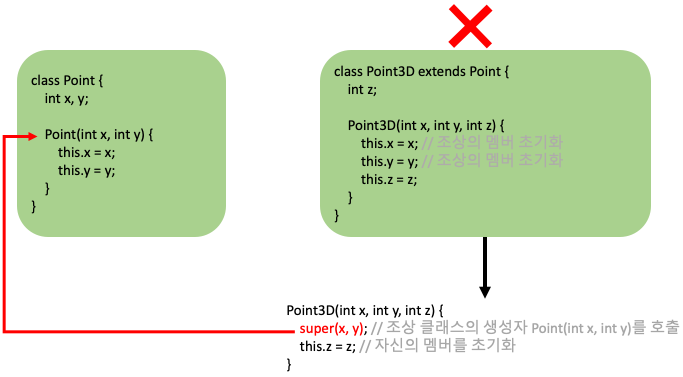
잘못된 코드
Point3D라는 자손의 생성자가 this.x = x;로 조상의 멤버를 초기화하고 있다 -> 안되는 것은 아니지만 비추천
자손의 생성자는 자신이 선언한 것만 초기화해야됨
-> super(x, y)와 같이 조상의 생성자를 호출해야됨
조상이 선언한 멤버를 초기화하려면
조상의 생성자를 호출해서 조상의 생성자가 조상멤버를 초기화해야됨
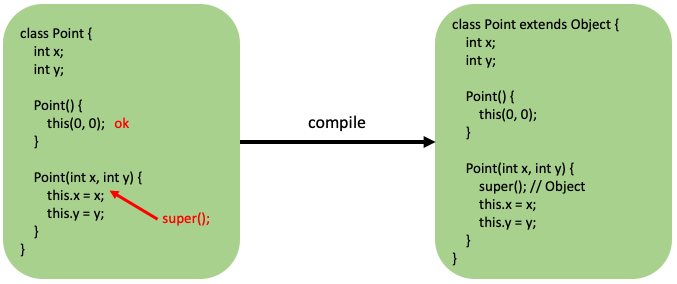
생성자 super()의 추가 조건
생성자의 첫 줄에 반드시 생성자(super, this)를 호출해야 한다
호출하지 않을 경우 컴파일러가 생성자의 첫 줄에 super();을 삽입한다
해당 코드의 경우 Object의 기본생성자를 호출함
에러 발생 코드
컴파일 에러: superPoint()라는 생성자가 없다
모든 생성자는 첫 줄에 다른 생성자를 생성해야하는 규칙을 안지켰기 때문
class superPoint {
int x;
int y;
superPoint(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
String getLocation() {
return "x :" + x + ", y :" + y;
}
}
class superPoint3D extends superPoint {
int z;
superPoint3D(int x, int y, int z) { // 에러 발생
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.z = z;
}
String getLocation() {
return "x :" + x + ", y :" + y + ", z: " + z;
}
}
public class PointTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
superPoint3D p = new superPoint3D(1, 2, 3);
}
}
에러코드 컴파일 할 경우
superPoint3D 클래스의 생성자가 첫 줄에 없고,
모든 생성자는 첫 줄에 다른 생성자를 생성해야하는 규칙 때문에super();를 넣어준다
이때 superPoint()의 기본 생성자가 없다
생성자가 1개 존재하기 때문에 기본 생성자를 컴파일러가 넣어주지 않는다
따라서 superPoint()의 기본생성자가 없다고 에러가 발생한다
* 클래스 생성할때 기본 생성자 작성은 필수이다 *
class superPoint extends Object {
int x;
int y;
superPoint(int x, int y) {
super(); // object();
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
String getLocation() {
return "x :" + x + ", y :" + y;
}
}
class superPoint3D extends superPoint {
int z;
superPoint3D(int x, int y, int z) {
super(); // superPoint() 호출
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.z = z;
}
String getLocation() {
return "x :" + x + ", y :" + y + ", z: " + z;
}
}
public class PointTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
superPoint3D p = new superPoint3D(1, 2, 3);
}
}
해결방법
1. superPoint() {} 생성자를 추가하거나,
2. 기본 생성자를 호출하지 않게 한다
super(x, y)로 바꿔준다: 기본 생성자가 아닌 superPoint()의 생성자를 호출하게 해준다
(조상의 멤버는 조상의 생성자가 초기화 해주는 것이 올바르기 때문)
// 2번 방법
superPoint3D(int x, int y, int z) {
// 조상의 생성자 Point(int x, int y)를 호출
super(x, y);
this.z = z;
}
완성 코드
class superPoint{
int x;
int y;
superPoint(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
String getLocation() {
return "x :" + x + ", y :" + y;
}
}
class superPoint3D extends superPoint {
int z;
superPoint3D(int x, int y, int z) {
super(x, y);
this.z = z;
}
String getLocation() {
return "x :" + x + ", y :" + y + ", z: " + z;
}
}
public class PointTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
superPoint3D p = new superPoint3D(1, 2, 3);
System.out.println(p.x); // 1
System.out.println(p.y); // 2
System.out.println(p.z); // 3
}
}'Java > 객체지향' 카테고리의 다른 글
| import 문, static import문 (0) | 2023.06.08 |
|---|---|
| 패키지(package) (0) | 2023.06.08 |
| 참조변수 super (0) | 2023.06.07 |
| 오버로딩(overloading) vs 오버라이딩(overriding) (0) | 2023.06.06 |
| 메서드 오버라이딩(overriding), toString을 사용하여 출력하기 (0) | 2023.06.06 |




