Iterator<E>
클래스를 작성할 때, Object 타입 대신 T와 같은 타입 변수를 사용
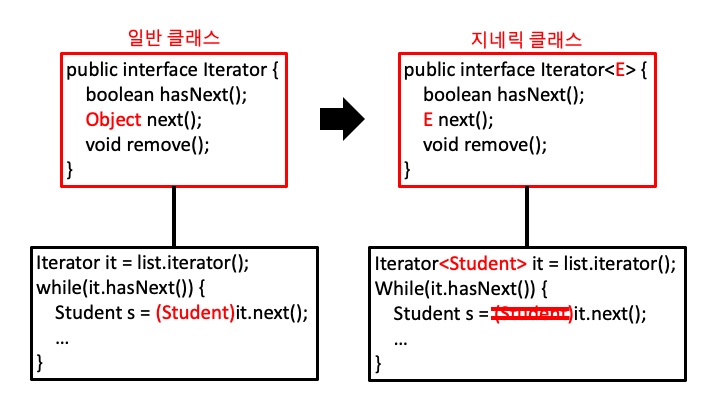
next()가 반환하는 것이 Object가 아닌 Student이기 때문에 형변환 불필요
import java.util.*;
class IteratorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Student> list = new ArrayList<Student>();
list.add(new Student("LG", 1, 1));
list.add(new Student("samsung", 1, 2));
list.add(new Student("apple", 2, 1));
Iterator<Student> it = list.iterator(); // 없을 경우 밑의 주석처럼 형변환 필요
while (it.hasNext()) {
// Student s = (Student)it.next(); // 지네릭스를 사용하지 않으면 형변환 필요.
Student s = it.next(); // next()가 반환하는 것이 Object가 아닌 Student이기 때문에 형변환 불필요
System.out.println(s.name);
// System.out.println(it.next().name); 위의 두 줄 한 줄로 줄이기
// System.out.println(((Student)it.next()).name); 형변환 할 경우 줄이기
}
}
}
class Student {
String name = "";
int ban;
int no;
Student(String name, int ban, int no) {
this.name = name;
this.ban = ban;
this.no = no;
}
}
LG
samsung
appleHashMap<K, V>
여러 개의 타입 변수가 필요한 경우, 콤마(,)를 구분자로 선언
HashMap<String, Student> map = new HashMap<String, Student>(); // 생성
map.put("Apple", new Student("Apple", 1, 1, 100, 100, 100)); // 데이터 저장

코드
import java.awt.dnd.DragGestureEvent;
import java.util.*;
class HashMapTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// HashMap<String, Student> map = new HashMap<String, Student>();
HashMap<String, Student> map = new HashMap(); // <String, Student> 생략 가능
map.put("Apple", new Student("Apple", 1, 1, 100, 100, 100));
Student s = map.get("Apple");
System.out.println(map); // {Apple=Student@7c75222b}
System.out.println(map.get("Apple").name); // Apple
}
}
class Student {
String name = "";
int ban;
int no;
int kor;
int eng;
int math;
Student(String name, int ban, int no, int kor, int eng, int math) {
this.name = name;
this.ban = ban;
this.kor = kor;
this.eng = eng;
this.math = math;
}
}
{Apple=Student@7c75222b}
Apple반응형